A Guide to Business Process Mapping

Business process mapping, also called business process analysis (BPA), helps you organize business processes by visually displaying the steps within a process from start to finish. It shows everything from “who”, “what”, “where”, “when” and “how” so you can analyze the “why.”
BPA is about analyzing business operation processes by creating a detailed, step-by-step identification of what works in your processes, where improvements can be made and how to make them.
Process mapping example
An example of a business process mapped in a visual flowchart could be how your organization brings on a new hire. Your new employee onboarding may include the following steps taken by your human resources (HR) team:
- Post a new job listing.
- Review and score resumes.
- Select candidates for interviews.
- Schedule interview(s).
- Score interviewed candidates.
- Send an offer or rejection.
- Negotiate a contract.
- Accept the signed and agreed offer letter.
- Prepare and provide training materials.
What Is Process Mapping?
Process mapping allows organizations to turn complex processes into step-by-step process maps that break down the structure of work. This detailed map can help you identify and weed out weak points, making it easier to streamline end-to-end work. It’s part of workflow management, which can include business process modeling.
Business process modeling is a more detailed representation of a process that captures and represents processes for analysis and decision-making. Think of it like this: the process map shows you on paper steps A, B and C, whereas a process model will zoom into step A, tell you every granular detail, and then do the same for steps B and C – leaving nothing out.
Process mapping techniques
Creating a process map may sound time-consuming, but there are ways of process mapping using automation technology. With tools such as process intelligence, process mining and task mining, you can record the steps within a task, including bottlenecks and those areas ripe for automation.
From there, automating those tasks with intelligent automation (IA) – also called business process automation or digital process automation – will help you get work done faster, with fewer errors and with your employees working on higher-value, non-repetitive tasks.
Business process mapping tools and solutions
Process mining software exists in many business process management (BPM) applications. BPM allows you to automate tasks while also connecting and orchestrating work across your business. A BPM platform such as SS&C | Blue Prism® Chorus BPM, also sometimes called business process orchestration, allows you to not only map your processes but also deploy intelligent automation (IA) into those processes to improve efficiency.
IA combines robotic process automation (RPA) and BPM to automate end-to-end business processes.
The stages of the BPM lifecycle

A BPM platform will simplify process mapping. The BPM lifecycle includes:
- Discovery: Process discovery, process mining, task mining, process intelligence, process modeling, process monitoring and documentation.
- Analysis: Documentation, data collection, process validation, resource allocation, validation testing and process intelligence.
- Design: Redesign, resource allocation and process models.
- Implementation: Documentation, deployment, testing and validation, feedback collection and performance evaluation.
- Improvement: Continuous adjustment and optimization.
How To Create a Process Map
Whether you create your process map on a piece of paper or use workflow management software, these are the details good process mapping includes:
Step 1: What are you mapping?
Select a process you want to map out. Maybe it needs to improve, or you want to share with a new team member what each step in the process requires.
Step 2: What’s happening in the process?
Document every task required to complete the chosen process. Create a detailed list of every activity and who performs each. We’d suggest you collaborate with other people in the business to ensure you don’t miss any steps and you’ve included all the important details.
Step 3: What’s the order of operations?
Arrange the list you compiled into the proper sequence of events so you can “map” out the entire process end-to-end. Look through the map and ensure you haven’t left any gaps.
Step 4: Create your flowchart
Now you can create a visual representation of how your process runs from start to finish. This will help give you an overview of the entire structure in a clear and manageable way.
Step 5: Review the process map
Once you’ve checked over the process map, share it with those involved in the process to ensure it’s accurate and easy to understand.
Step 6: What can you improve?
Now’s the time to analyze your process workflow and find ways to improve it. You can use tools for this or do it manually. Look for bottlenecks, inefficiencies, unnecessary complexities and opportunities for improvement.
Step 7: Enact your improvements
With your opportunities identified, you can now start implementing incremental changes to make your process run smoother. This is a continuous effort, and you’ll find yourself employing these seven steps throughout your business.
Benefits of Business Process Mapping
There is a point to all this effort. You can only improve what you understand, and process mapping helps you do that. With a detailed look into as-is processes, you can:
- Find missing pieces.
- Simplify complex steps.
- Help your people better understand their work.
- Delegate responsibilities and resources more effectively.
- Create documentation and monitor progress.
- Make decisions faster.
- Streamline communication and actions.
- Meet compliance and regulatory standards easier.
- Achieve better transparency and visibility.
The added benefit of using BPM for this is that you get all those positive results but faster and without the risk of human error or missed information.
Why use a process map?
A prosperous business is one that always has an ear to the ground, observing how the organization functions and finding ways to continuously implement business process improvement. It will also help you prepare for automation.
The ultimate goal is business process optimization. Business process optimization (BPO) focuses on improving your business’s efficiency, effectiveness and adaptability by optimizing its existing processes strategically.
Types of Process Mapping
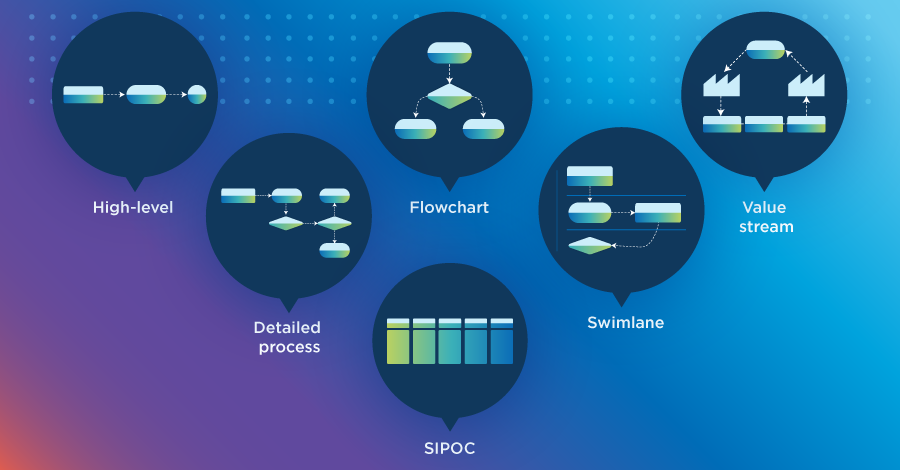
Some of these process maps may be familiar to you. What’s important is finding one that best suits your business process layout, to the level of your complexity, ensuring it’s clear and understandable to the people in your business.
Flowchart
A basic flowchart uses simple process mapping symbols to show how a process flows, including the process’s inputs and outputs and any steps within. It shows how a process is done from start to finish, usually in order.
Use for: planning new projects, explaining a process to team members, solving problems and managing workflows.
High-level
A high-level process map or top-down map shows a high-level overview of a process. It may show fewer steps and focus on the essential pieces with minimal detail.
Use for: Communicating the basic steps in a process.
Detailed
A detailed process map shows a layered level of details including each step and subprocess. It documents every decision point, showing the inputs and outputs within each step. This is the most thorough process map.
Use for: Pinpointing inefficiencies and providing comprehensive process details.
Swimlane
A swimlane map, also called a deployment flowchart or cross-functional flowchart, puts process activities into swimlanes and shows who is responsible for each task. The map is divided into channels based on each stakeholder and lists each of their activities. A swimlane map is great for new employees to learn their roles in a process.
Use for: Highlighting the roles and responsibilities involved in a process.
Value stream
A value stream map illustrates how a product or service is brought to a customer. These maps tend to be complex due to the number of materials within the process.
Use for: Describing how a product or service is presented quantitatively to a customer.
SIPOC
Suppliers, inputs, process, outputs and customers (SIPOC) is a diagram or chart that identifies the key areas of a process and may be used as a first step toward creating a more detailed process map. It features five columns depicting the basic steps and details of the process.
Use for: Defining complex processes and identifying critical areas and people in a process.
Continuously Improve
By automating this work, you’ll realize the benefits of process mapping sooner, and make IA deployment even easier. Relieve your employees from slow, inefficient processes and get your operations in tip-top shape.
Orchestrate your organization’s digital transformation and set yourself up for success with BPM. Read our BPM e-book to discover more.
